PFSK151 3BSE018876R1控制板卡,ABB产品尺寸
总线错误处理由于不同的条件可能导致总线错误异常,因此软件必须能够区分来源。为了帮助实现这一点MVME147在VMEchip和PCC芯片中提供状态位。通常,总线错误处理程序可以查询状态位和继续查看结果。然而,有两个条件会破坏
状态位:❏ 总线执行期间可能发生中断错误处理程序(在指令可以写入状态之前寄存器以提升中断掩码)。如果中断服务例程导致第二个总线错误,该状态指示第一个总线错误的来源可能丢失。软件必须为解决这个问题而写。
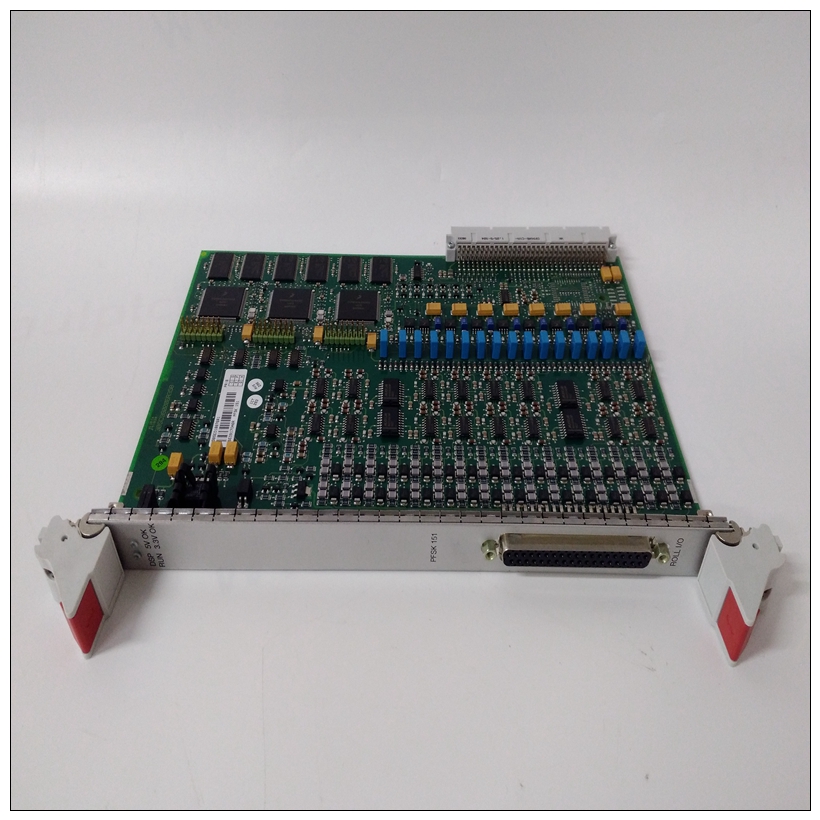
PFSK151 3BSE018876R1控制板卡PCC可以编程为发生总线错误时,生成7级中断。这
当总线连接时,可能有助于将MC68030强制到已知位置出现错误。
❏ PCC可以采用VMEbus绑定的BERR*(更新MC68030接收和处理之间的状态位)
总线错误,反之亦然。MC68030执行需要不可分割周期的操作序列到本地DRAM和VMEbus。MVME147需要特殊电路来支持这些操作。不可分割的对单个地址的访问称为单地址读修改写周期(SARMC)。对多个地址的不可分割访问称为多地址读修改写周期(MARMC)。SARMC周期(由测试和设置(TA)和单字节引起比较和交换(CAS)指令)完全受MVME147。这是可能的,因为VMEbus定义了这样的周期。MARMC循环(由CAS2和多字节CAS指令引起
和MMU桌面行走)有条件地由MVME147。VMEbus不定义这些周期。PCC中的WAITRMC位控制MARMC的支持周期。如果WAITRMC被清除,则不能保证MARMC循环不可分割。此外,如果MARMC循环跨越船上DRAM和VMEbus内存,MVME147出现故障。如果设置了WAITRMC,则保证MARMC循环是不可分的只有当其他VMEbus板实现其MARMC循环时与MVME147相同(带有WAITRMC集合)。注意,设置WAITRMC位可能是性能损失。当钻头设置后,MVME147等待成为VMEbus主控执行任何MARMC循环(即使它可能只执行车载DRAM)。
Bus Error Processing
Because different conditions can cause bus error exceptions, the
software must be able to distinguish the source. To aid in this, the
MVME147 provides status bits in the VMEchip and PCC chip.
Generally, the bus error handler can interrogate the status bits and
proceed with the result. However, two conditions can corrupt the
status bits:
❏ An interrupt can happen during the execution of the bus
error handler (before an instruction can write to the status
register to raise the interrupt mask). If the interrupt service
routine causes a second bus error, the status that indicates the
source of the first bus error may be lost. The software must be
written to deal with this. The PCC can be programmed to
generate a Level 7 interrupt when a bus error occurs. This
may help force the MC68030 to a known place when a bus
error occurs.
❏ The PCC can take a VMEbus bound BERR* (which updates
the status bits) between the MC68030 receiving and handling
of a bus error, or vice-versa. The MC68030 performs operations that require indivisible cycle
sequences to the local DRAM and to the VMEbus. The MVME147
requires special circuitry to support these operations. Indivisible
accesses to a single address are called Single Address Read-ModifyWrite Cycles (SARMC). Indivisible accesses to multiple addresses
are called Multiple Address Read-Modify-Write Cycles (MARMC).
SARMC cycles (caused by Test and Set (TAS) and single byte
Compare and Swap (CAS) instructions) are supported fully by the
MVME147. This is possible because the VMEbus defines such
cycles.
MARMC cycles (caused by CAS2 and multi-byte CAS instructions
and by MMU table walking) are conditionally supported by the
MVME147. The VMEbus does not define these cycles.
The WAITRMC bit in the PCC controls the support of MARMC
cycles. If WAITRMC is cleared, MARMC cycles are not guaranteed
to be indivisible. Furthermore, if MARMC cycles straddle onboard
DRAM and VMEbus memory, the MVME147 malfunctions.
If WAITRMC is set, MARMC cycles are guaranteed to be indivisible
only if the other VMEbus board implements its MARMC cycles the
same way as the MVME147 (with WAITRMC set). Note that setting
the WAITRMC bit can be a performance penalty. When the bit is
set, the MVME147 waits to become VMEbus master before it







